Why is the Sky Blue? And Why Are Sunsets Red?
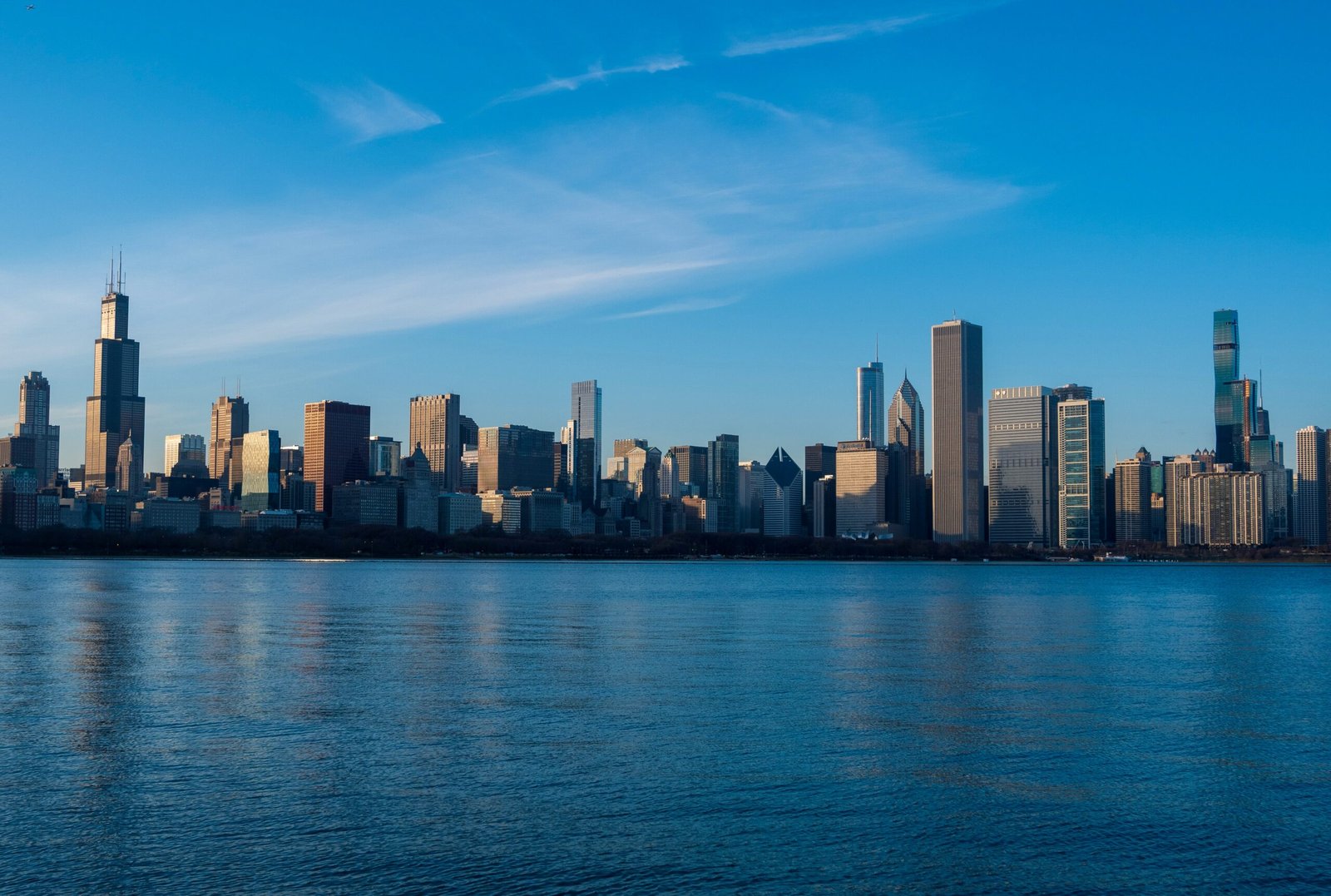

On a clear day, the Chicago skyline looks stunning against a deep blue sky. But have you ever stopped to ask—Why is the sky blue? Or why do sunsets glow red? Kids love these questions, yet we often shrug them off. Some believe the sky is blue because it reflects the ocean. Then why do we see fiery reds and oranges at sunset? The truth is, the sky isn’t any color—it just appears that way because of how sunlight interacts with our atmosphere.
The Science of Color and Light
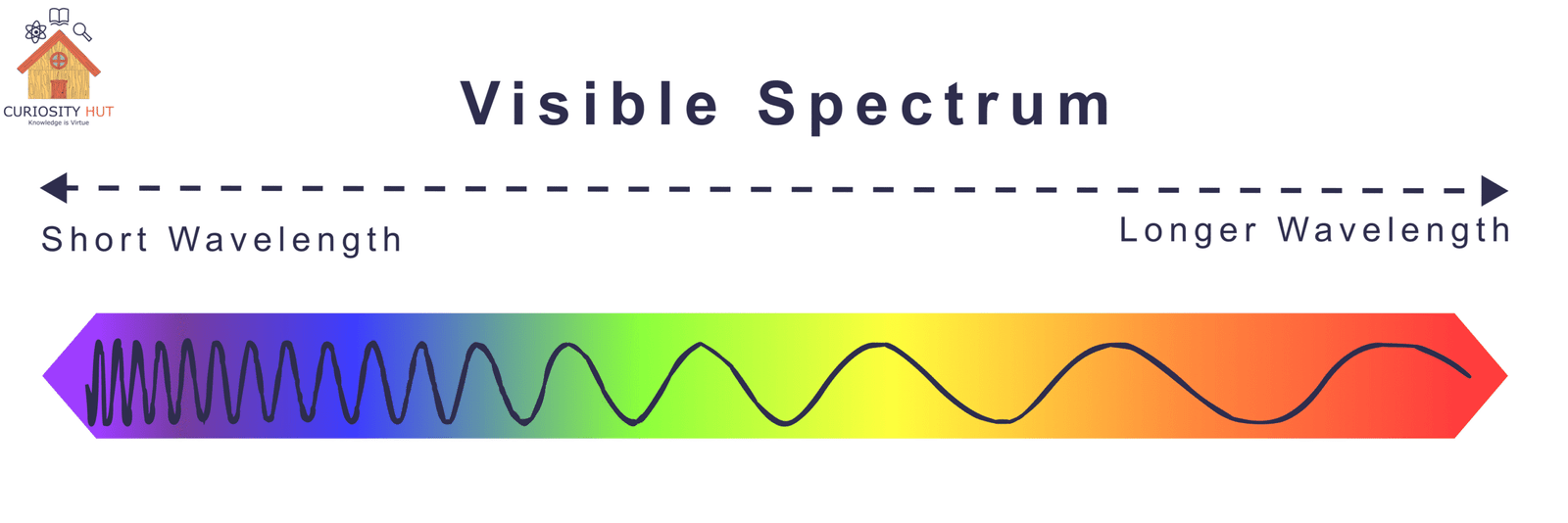
Everything we see either emits or reflects light. Light travels in waves, and different colors correspond to different wavelengths. Red light has the longest wavelength, while blue and violet have much shorter ones. Our eyes perceive colors based on which wavelengths are absorbed, reflected, or scattered by objects and the atmosphere. The sun’s light contains all colors of the rainbow, and when combined, they appear white. But once sunlight enters our atmosphere, things get interesting.
Air molecules—mostly nitrogen and oxygen—scatter sunlight in all directions. This effect, called Rayleigh scattering, is strongest for shorter wavelengths like blue and violet. As a result, blue light gets scattered more, raining down from all directions and making the sky appear blue.
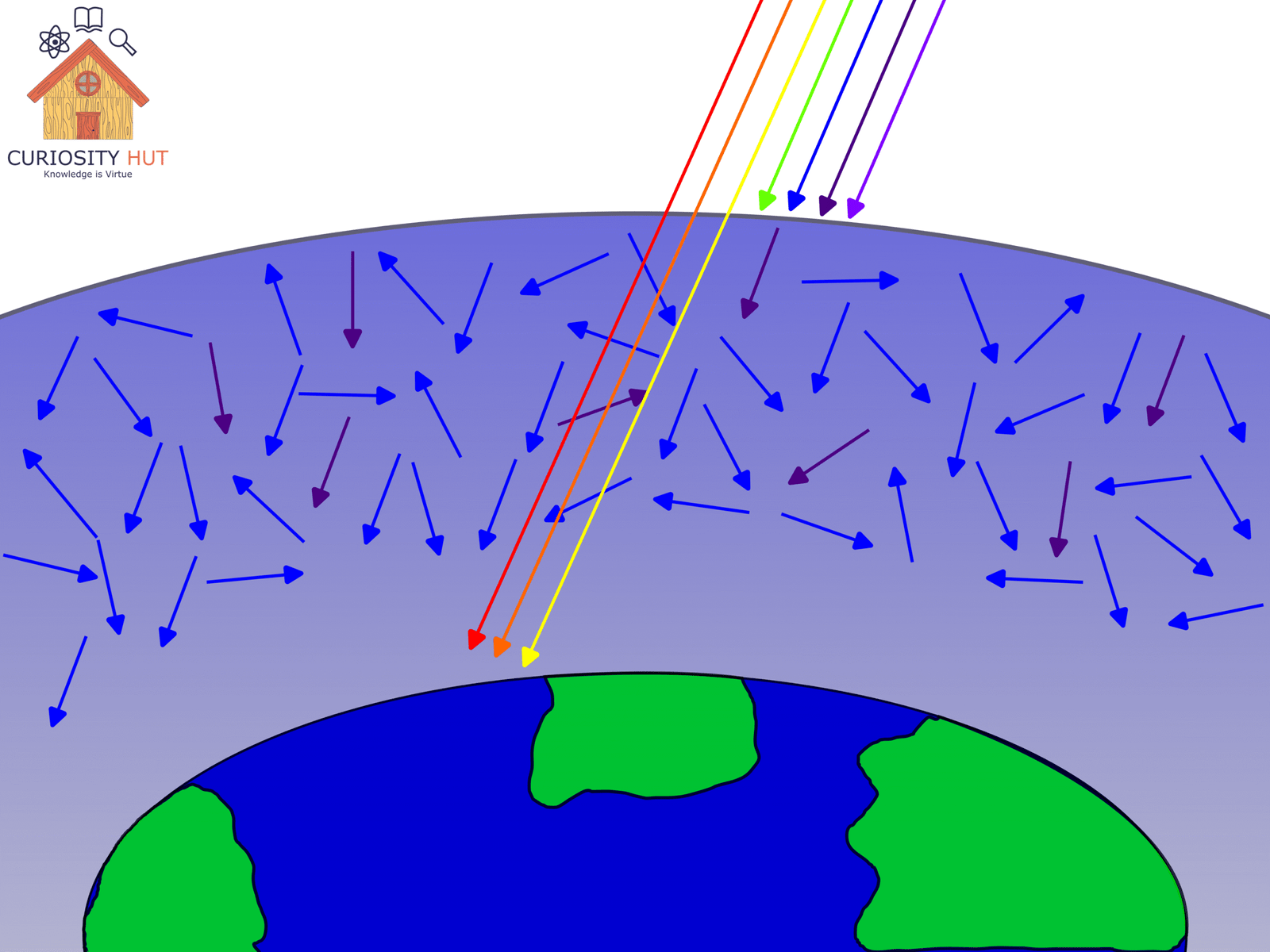
But why not purple? Two reasons: First, the sun emits more blue light than violet. Second, our eyes are more sensitive to blue, so that’s the color we perceive most.
Subscribe to my Free Newsletter
Sign up for blog updates, science stories, riddles, and occasional musings. No algorithms—just me, writing to you.
Why the Sun Looks Yellow
If blue light scatters in all directions, what’s left? Mostly red and green light, which mix to create yellow—the color we see when we look at the sun. You can even test this yourself using an RGB color mixer. Please don’t look at the sun.
Why Sunsets and Sunrises Look Red
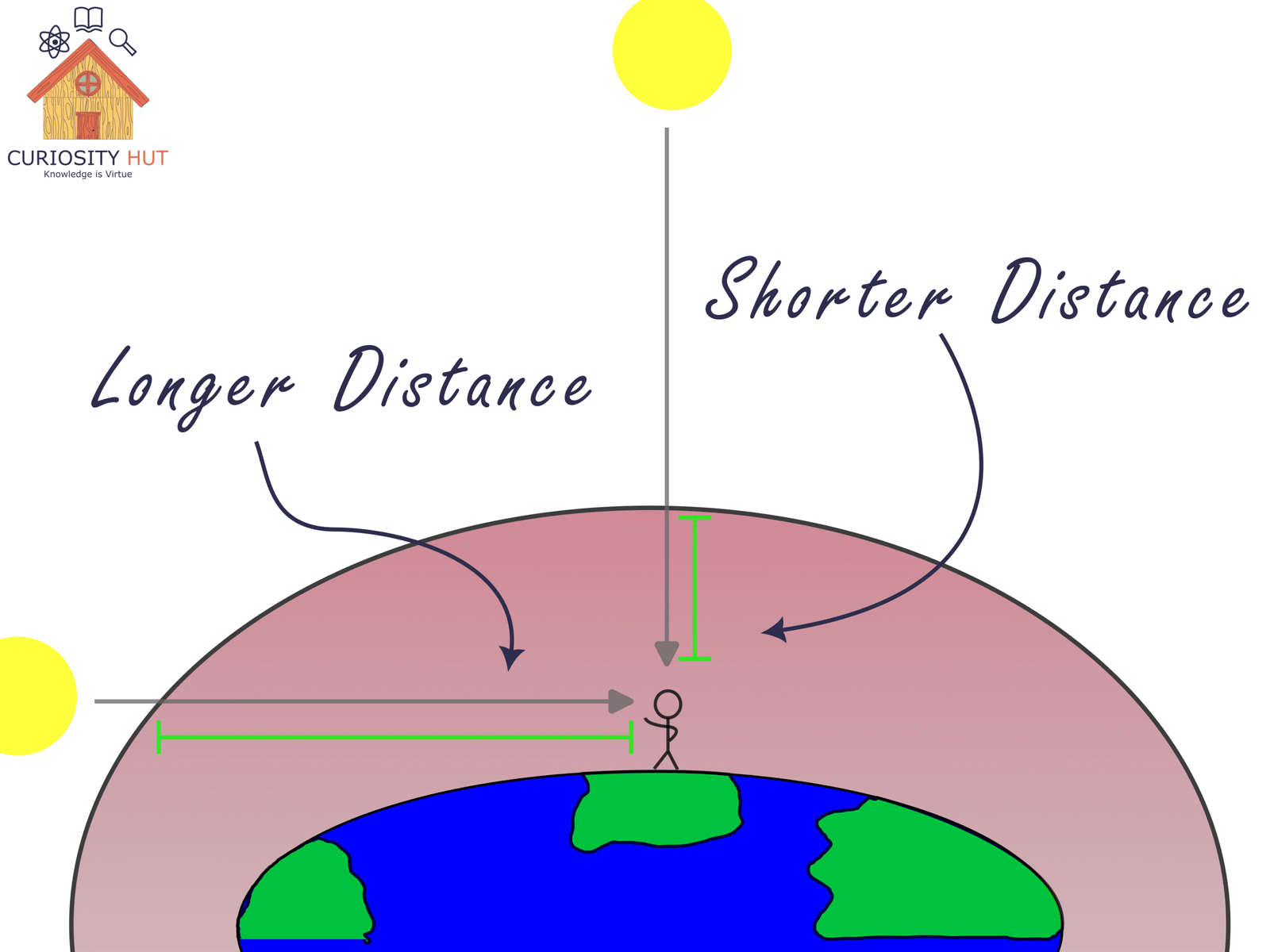
As the sun nears the horizon, its light must travel through more of Earth’s atmosphere. By the time it reaches us, blue, violet, and even green light have been completely scattered away. What remains? A breathtaking blend of red, orange, and yellow hues.
Can the Sky Ever Be Green?
Yes—under rare conditions. If the sun is low and a storm is on the horizon, red light can get absorbed by water droplets, leaving behind a ghostly green sky. This eerie phenomenon is more common in the Midwest and on islands where the horizon stretches far.
But Why Is the Ocean Blue?
If the sky isn’t blue because of the ocean, what about the other way around? In shallow waters, the seafloor affects color—sand makes water turquoise, and rocks add a greenish tint. But deep water is always blue. That’s because red wavelengths get absorbed first, leaving blue light to reflect back to our eyes.
Next Time Someone Asks…
So next time a curious kid asks why the sky is blue, you’ll know the answer: Shorter wavelengths scatter more in our atmosphere due to Rayleigh scattering. Or, if you want to keep it simple—because physics is awesome.
Subscribe to my Free Newsletter
Sign up for blog updates, science stories, riddles, and occasional musings. No algorithms—just me, writing to you.